ọdịnaya
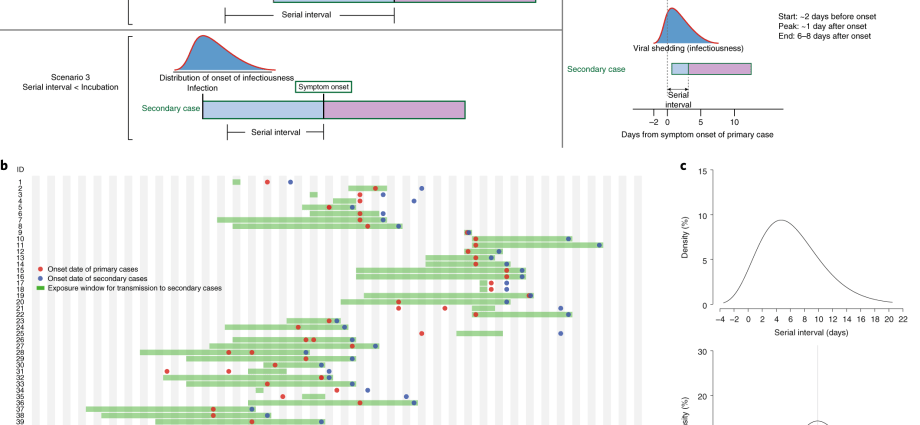
It is known that symptoms of coronavirus infection appear two to 14 days after infection. But when is someone with COVID-19 the most contagious? This is what researchers at the University of St Andrews in Scotland found out.
- The number of active particles of the viral genetic material was greatest at the onset of symptoms or during the first five days after onset
- No “live” virus was detected after the ninth day of illness
- Early isolation is critical to contain the spread of the coronavirus
- In an infected person, the highest density of the SARS-CoV-2 coronavirus may occur before the first symptoms appear
- Ị nwere ike ịchọta ihe ndị ọzọ gbasara coronavirus na ibe ụlọ TvoiLokony
When is the “peak infectivity” – scientists’ findings
The incubation period of the coronavirus, i.e. the time between its entry into the body and the first symptoms, is two to 14 days (most often it is five to seven days).
However, researchers from the University of St Andrews asked themselves: when does SARS-CoV-2 infected become the most contagious? In other words, when are COVID-19 patients “infectious”? Identifying the most likely time frames is fundamental to contain the spread of the coronavirus. It equips us with knowledge which stage of isolation is the most important here.
- Ndị ọkà mmụta sayensị nke Polish Academy of Sciences: ọnọdụ ahụ adịla egwu, ọ dị mkpa ịgbanwe usoro nnwale maka ọnụnọ SARS-CoV-2.
In search of an answer to this question, British scientists analyzed, among others. 79 global studies on COVID-19, which covered over 5,3 thousand hospitalized symptomatic patients (these included, inter alia, data on the duration of viral excretion and its viability). Based on the information collected, the researchers calculated the mean duration of SARS-CoV-2 excretion.
Ị bu ọrịa coronavirus ma ọ bụ onye dị gị nso nwere COVID-19? Ma ọ bụ ikekwe ị na-arụ ọrụ na ọrụ ahụike? Ọ ga-amasị gị ịkesa akụkọ gị ma ọ bụ kọwapụta mmebi iwu ọ bụla ị hụrụ ma ọ bụ emetụta? Dee anyị akwụkwọ na: [Email na-echebe]. Anyị na-ekwe nkwa na amaghị aha!
Researchers also took samples from the throats of patients whose infection had not started earlier than nine days ago, as reported by the BBC, and then identified and recreated a viable pathogen. It turned out that the number of active RNA particles (fragments of viral genetic material) was greatest at the onset of symptoms or for the first five days after onset.
Meanwhile, inactive viral RNA fragments were found in nasal and throat samples up to an average of 17 days after the onset of symptoms. However, despite the persistence of these fragments, no studies have detected a “live” virus after the ninth day of illness. Therefore, it is unlikely that the risk of infection will be high in most sick people beyond this point.
The conclusion from this study is that early-stage patients are most contagious, and that a “live”, replication-competent virus is present for up to nine days after the onset of symptoms. Early isolation is therefore critical to contain the spread of SARS-CoV-2.
“People need reminders that isolation is necessary as soon as symptoms, even mild ones, appear,” said Dr. Muge Cevik of the University of St Andrews. There is a risk that before some people get SARS-CoV-2 test results and quarantine themselves, they will unknowingly pass the phase when they are most infected.
One of the most effective protection against SARS-CoV-2 infection is covering the face and nose. Check the offer of disposable masks at a lower price, which you can buy at medonetmarket.pl.
To find out if the symptoms we notice in ourselves or in our loved ones are a sign of coronavirus infection, do a COVID-19 Shipping Test.
Patients can become infected before they develop symptoms. When is the greatest risk?
However, the study of Scottish scholars did not include asymptomatic people. Scientists warn, however, that patients can become contagious before they develop any symptoms of SARS-CoV-2 infection.
Some studies have found that people are most contagious just before symptoms start and in the first week of being infected with the virus.
- Kedu ihe mgbaàmà nkịtị na nke a na-ahụkarị nke COVID-19? [Anyị na-akọwa]
The president of the Polish Society of Epidemiologists and Doctors of Infectious Diseases, prof. Robert Flisiak. – In an infected person, the highest density of the SARS-CoV-2 coronavirus occurs even before the first symptoms appear, which is why such people are the most contagious – he warned during a virtual press conference. – This is the biggest reason for this epidemic spreading so fast in a way that is difficult to control. Because we are not able to control people who do not yet have symptoms of infection, which is when it is most contagious. And when symptoms do appear, we already have a decrease in the risk of infectivity – explained the specialist (more on this topic).
He reminded that the infected can quickly spread the infection to others, especially when the rules of prophylaxis are not followed – wearing masks, keeping an appropriate distance, and hand hygiene and disinfection.
Ị na-achọ ihe mkpuchi na-adịghị emerụ gburugburu ebe obibi? Lelee ihe mkpuchi ihu mbụ nwere ike imebi n'ahịa, dị na ngwugwu ọnụ.
Ị nwere ike ịmasị:
- Kedu ka nguzogide COVID-19 nwere ike ịdịgide? Nchọpụta ọhụrụ ahụ na-eweta ahụ efe. "Akụkọ na-atọ ụtọ"
- British government: ventilate apartments often for 10-15 minutes! This is important in the fight against COVID-19
- Kedu ihe kpatara anyị ji eme obere nnwale COVID-19? Dị ka minista ahụike si kwuo, nke a bụ ihe na-egosi na ọnọdụ ahụ na-akawanye mma
Ọdịnaya nke webụsaịtị medTvoiLokony bu n'obi imeziwanye, ọ bụghị dochie anya kọntaktị dị n'etiti Onye ọrụ weebụsaịtị na dọkịta ha. Ezubere webụsaịtị ahụ maka ebumnuche ozi na naanị nkuzi. Tupu ịgbaso ihe ọmụma ọkachamara, karịsịa ndụmọdụ ahụike, dị na weebụsaịtị anyị, ị ga-agarịrị dọkịta. Onye nchịkwa anaghị ebute nsonaazụ ọ bụla sitere na iji ozi dị na weebụsaịtị. Ị chọrọ ndụmọdụ gbasara ahụike ma ọ bụ ndenye ọgwụ e-redee? Gaa na halodoctor.pl, ebe ị ga-enweta enyemaka n'ịntanetị - ngwa ngwa, n'enweghị nsogbu na ịhapụ ụlọ gị.